04 August 2025
Hull Construction: Overview of Yacht Components
For newcomers to the community of sailing enthusiasts, or for seasoned owners who want to consolidate their knowledge, it's essential to understand the hull construction and key terminology of a yacht. This will help you to better operate and maintain your yacht, as well as communicate efficiently with others in case of an emergency. In this article, we'll give you a detailed overview of the various parts of a yacht and their functions, to help you quickly get to the heart of yacht construction.
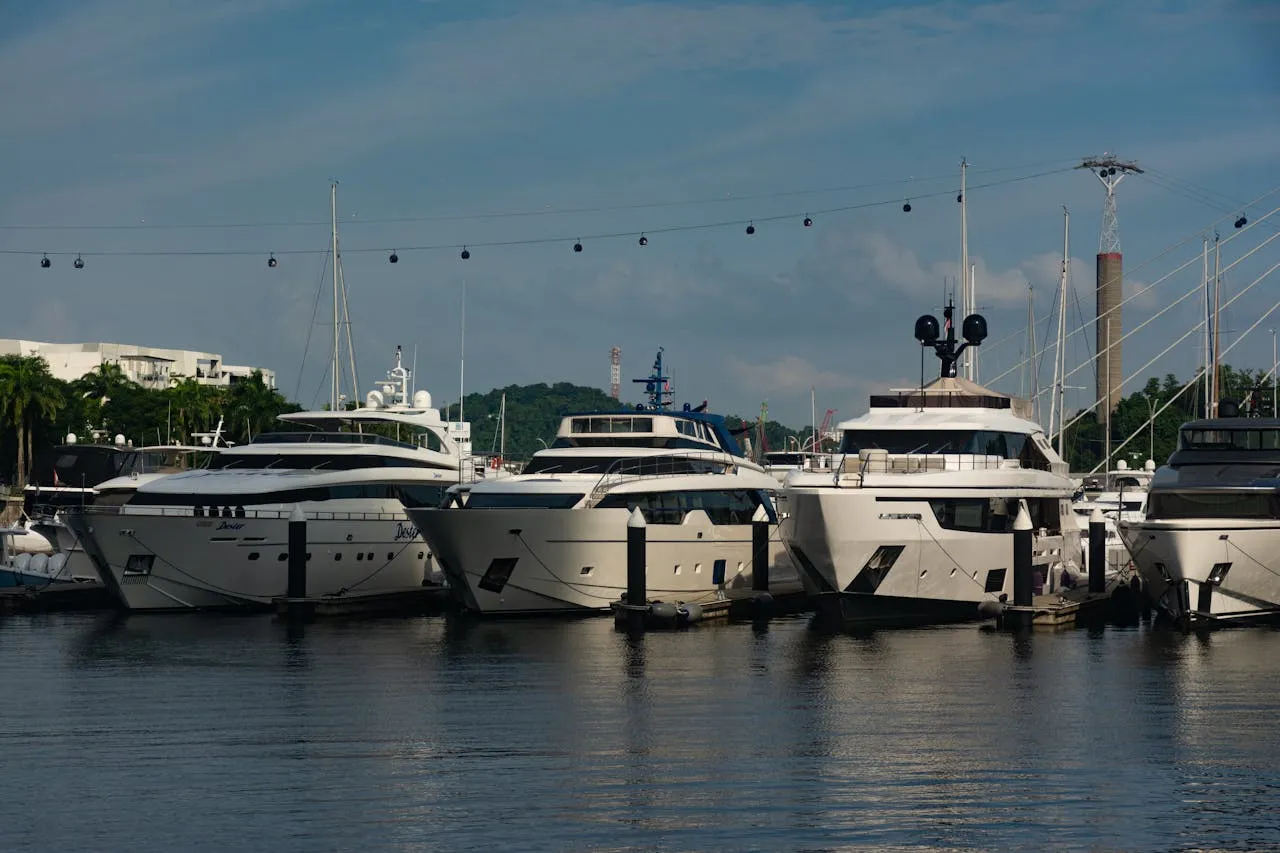

Overview of the Main Structure of a Yacht
The construction of a yacht is complex and subtle, with each component serving a unique purpose. Here are some basic but key construction terms:
Bow: The part of the yacht's bow that points straight ahead when the yacht is moving forward, and serves as a pointer to the direction in which the yacht is travelling.
Stern: the rear part of the yacht that houses the engine and also has storage space, seating, and even a swim platform for passengers to move around.
Port and Starboard: The left side of the yacht is called the port side and the right side is the starboard side, the starboard side is often the side where the captain is located, which is easy to command and operate.
Cockpit: The central area where the captain controls the yacht, complete with engine controls, joystick or steering wheel.
Hull: The main structure of the yacht, providing buoyancy and enabling the yacht to float on the water. Hulls come in a variety of designs, some glide over the water and others propel through the water.
Ledge: Where the hull meets the deck on either side, it is the edge part of the yacht that protects the passengers.
Keel: the beam that extends from the bow to the stern and guides the yacht to stabilise its progress in the water.
Propeller: A metal blade shaped like a fan located at the bottom of the yacht that rotates to propel the yacht forward.
Deck: The area above the hull where passengers can walk and move around, larger yachts will have more than one deck to suit different needs.
Cabin: The living area where passengers sleep and conduct indoor activities.
Cockpit: where the captain's controls and electronics are located, and also serves as the captain's workstation.
Kitchen & Bathroom: The kitchen on a yacht is usually located below deck in the cabin, but also on deck; the bathroom is almost always located below deck for the convenience of the passengers.
Yacht Key Distances and Dimensions
Knowing the key distances and dimensions of a yacht is essential for sailing safety. Here are some of the parameters that must be mastered
Breadth: the width of the yacht from port to starboard at its widest point, which determines the stability and passageability of the yacht.
Draught: the distance from the waterline (where the yacht touches the water) to the keel at the bottom of the boat, which affects the yacht's ability to navigate in different waters.
Dry side: the distance from the waterline to the sides of the yacht's flanks, reflecting the yacht's wave protection.
Other Important Yacht Components
In addition to the basic construction described above, there are many other key yacht components, each with its own unique function:
Anchor: a large metal device that secures the yacht's position by sinking into the water to prevent drifting.
Awnings: retractable shelters made of canvas or other materials that protect passengers on deck from inclement weather.
Ballast: Extra weight added to stabilise a yacht to improve its stability underway.
Bilge: the area at the bottom of the yacht near the bathroom shower area, used to collect excess water and keep the interior of the yacht dry.
Bulkheads: Upright support structures or walls inside the hull that connect key compartments and increase the structural strength of the yacht.
Waveguard: A design on the edge of the cockpit that prevents water from splashing into the cockpit and protects electronic equipment from damage.
Console: A gathering area above the deck or cockpit that centralises a variety of controls for easy operation.
Dinghy: Also known as an accessory boat, a small vessel used for travelling to and from land or inshore areas, usually carried by the mother ship.
Flybridge: a cockpit on top of the cabin of a large yacht, providing a wider view and a more comfortable driving experience.
Hatch: A small opening that connects the cabin area to the deck, allowing easy access to the cabin.
Porthole: A window on a yacht, usually circular, providing natural light and ventilation.
Rudder: a flat part vertically articulated near the stern for steering, the steering wheel of a yacht.
Swimming platform: a platform near the stern of the boat that makes it easy for passengers to jump into the water and climb back aboard for fun on the water.
Side Thrusters: used to move large yachts to either side without moving forward or backward, improving the yacht's manoeuvrability.
Common Sailing Terms
While sailing with a yacht, you will also come across some terms for non-physical parts that are equally important:
Rigging: another word for rope, used to secure the yacht or attach other equipment.
Bollard: a metal device used to secure and fasten a cable to ensure the safety of a yacht when moored.
Moorings: areas for yachts to dock safely, e.g. pontoons, berths, etc.
Rigging: special ropes used to manoeuvre sails, masts and transoms, essential for sailing.
Waterline: where the water meets the hull, reflecting the yacht's draft.
Mastering these basic constructions and key terms is the first step towards professionalism for every yachtsman. By understanding the role of each hull component, you can improve your operating skills and also make more rational judgement in the process of yacht maintenance, repair and trading. If you have more questions about yacht construction, welcome to get professional one-stop consulting and service through Yachttrading platform.
 Report
ReportNetizen comment
Comments

Leave the comment
Relevant Recommendation
Yacht Info
Most Recommended